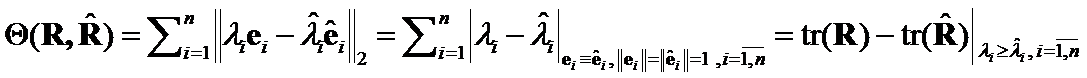The Theta Criteria methods for positively defined ![]() matrices were introduced in [1] - [4]. Those criteria have been constructed on norms of differences of matrices ordered weighted eigenvectors. We will now study Theta Criteria properties in depth.
matrices were introduced in [1] - [4]. Those criteria have been constructed on norms of differences of matrices ordered weighted eigenvectors. We will now study Theta Criteria properties in depth.
Let ![]() is real numbers field,
is real numbers field,
![]() -finite linear vector space over
-finite linear vector space over ![]() ,
, 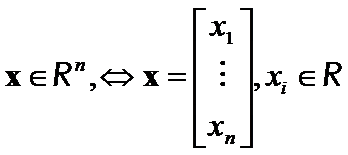 and
and![]() -set of all positively defined matrices of order
-set of all positively defined matrices of order ![]() . Let block matrices
. Let block matrices 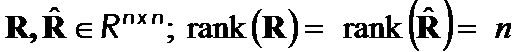 ,
, 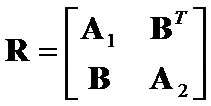 ,
, 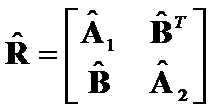 (1)
(1)
sub matrices 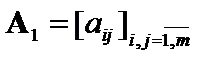 ,
,  ,
, 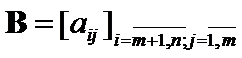 and
and 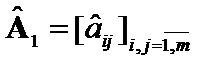 ,
,  ,
, 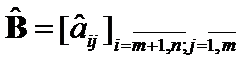 .
.
Let 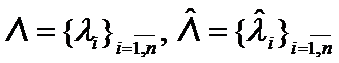 - sets of all ordered eigenvalues of
- sets of all ordered eigenvalues of  :
:
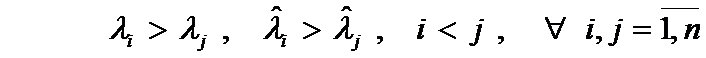 , (2)
, (2)
and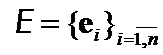 and
and 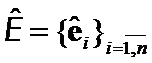 sets of all
sets of all  orthonormalized eigenvectors.
orthonormalized eigenvectors.
Let 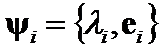 - eigenpair of
- eigenpair of ![]() and
and ![]() and
and  , with
, with 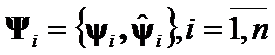
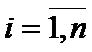 - a set of pairs of eigenpairs of
- a set of pairs of eigenpairs of ![]() -th eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
-th eigenvalues and eigenvectors of  .
.
Let 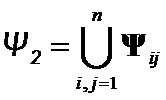 ,
, 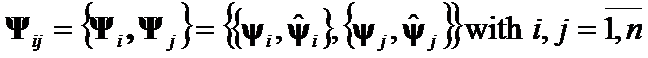 be a set of two pairs of eigenpairs of
be a set of two pairs of eigenpairs of ![]() -th and j-th eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
-th and j-th eigenvalues and eigenvectors of  and
and 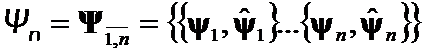 has been composed on
has been composed on ![]() eigenpairs
eigenpairs 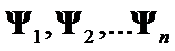 .
.
The forward differences ![]() of the determinants and condition numbers were used as matrices closeness criteria [5] - [9]:
of the determinants and condition numbers were used as matrices closeness criteria [5] - [9]:
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
The ![]() criteria of
criteria of  has been introduced in [4]:
has been introduced in [4]: 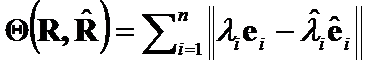 . (5)
. (5)
Let ![]() be a limited linear, self-conjugated integral matrix from space
be a limited linear, self-conjugated integral matrix from space ![]() into
into ![]() and
and
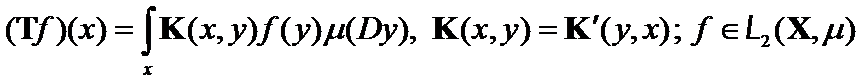 where
where![]() is the matrix's kernel. There exist
is the matrix's kernel. There exist ![]() representations on orthonormalized matrices of eigenfunctions
representations on orthonormalized matrices of eigenfunctions 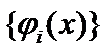 and eigenvalues
and eigenvalues 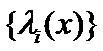 of
of ![]() as follows:
as follows:
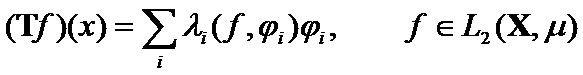 (6)
(6)
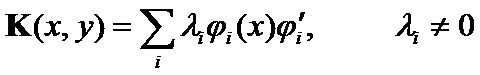 (7)
(7)
The series are converging on norms ![]() respectively [10] - [12].
respectively [10] - [12].
Let us construct ![]() criteria between
criteria between  , or
, or 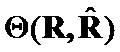 , which can converge on
, which can converge on ![]() . Such criteria will reflect the geometrical changes on some the elements of
. Such criteria will reflect the geometrical changes on some the elements of ![]() ,
, ![]() … or
… or ![]() . The proper choice of
. The proper choice of ![]() criteria depends on a priori information about
criteria depends on a priori information about  structures and their distinction type. If all elements of
structures and their distinction type. If all elements of ![]() have changed, then
have changed, then 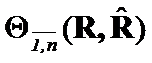 is appropriate choice. If only
is appropriate choice. If only 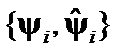 and
and  have changed, then
have changed, then 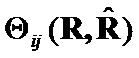 is acceptable. Now we can formulate several hypotheses about matrices
is acceptable. Now we can formulate several hypotheses about matrices  differences.
differences.
Hypothesis I: The matrices  distinctions can be represented by geometrical differences between
distinctions can be represented by geometrical differences between ![]() and
and ![]() of
of 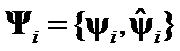 .
.
Then Euclidean norm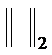 of
of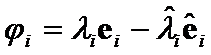 can serve as
can serve as 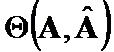 or
or
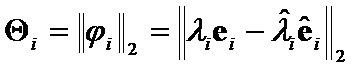 .(8)
.(8)
Hypothesis II: The matrices  distinction is represented by geometrical differences between
distinction is represented by geometrical differences between 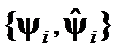 and
and 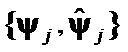 of
of 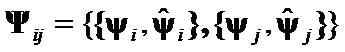 .
.
Then the sum of 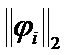 and
and  can serve as
can serve as 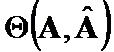 :
:
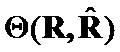 =
= (9)
(9)
Hypothesis III: The matrices  distinction is represented by geometrical differences between
distinction is represented by geometrical differences between  of
of 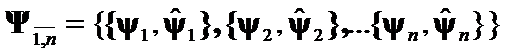 .
.
Then the sum of 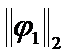 ,
, 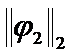 …
… can serve as
can serve as 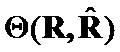 :
: 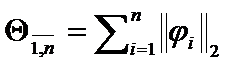 . (10)
. (10)
According to [9], a real-valued function ![]() on linear space
on linear space ![]()
![]() is
is ![]() on
on ![]() , if
, if
 (Positivity) (11)
(Positivity) (11)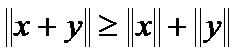 (Triangle inequality) (12)
(Triangle inequality) (12) 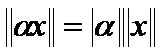 (Homogeneity) (13)
(Homogeneity) (13)
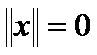 if and only if
if and only if ![]() .(Positive definiteness) (14)
.(Positive definiteness) (14)
Theorem 1. (Positivity).
The criteria  .
.
Proof: From ![]() criteria definition and Euclidean norm properties
criteria definition and Euclidean norm properties
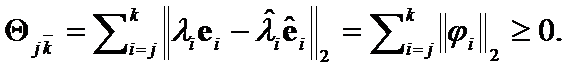
Q.E.D.
Theorem 2.(Triangle inequality)
If 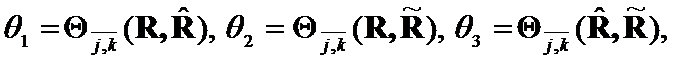
 , then
, then  .
.
Proof: According to 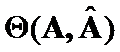 definition,
definition, 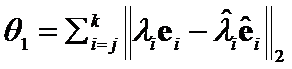 ,
,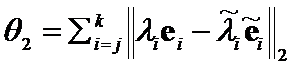 ,
, .
.
Since  , the vectors
, the vectors 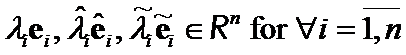 . Then
. Then 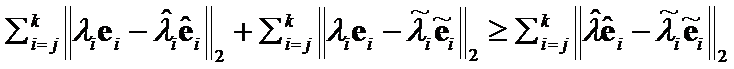 .
.
Q.E.D.
Theorem 3.(Homogeneity):
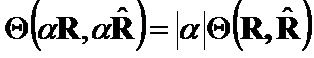 ,where
,where![]() .
.
Proof: Since 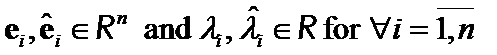 ,
,
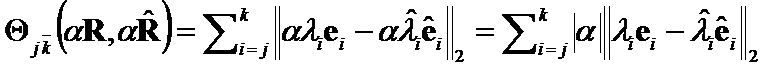
Q.E.D.
Theorem 4. (Positive definiteness)
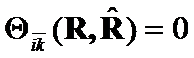 if and only if
if and only if![]() .
.
Proof: Let ![]() . The
. The  criteria is
criteria is 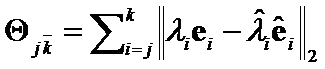 . The
. The ![]() -th component of
-th component of  is
is
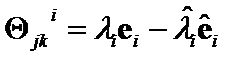 . According to [2], [3] and Hilbert Theorem
. According to [2], [3] and Hilbert Theorem 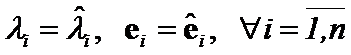 and
and 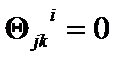 .
.
Then 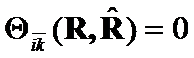 is true, because index
is true, because index ![]() is arbitrary.
is arbitrary.
Let 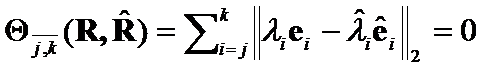 .
.
Then we will receive the system of ![]() equations
equations
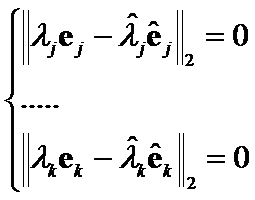
with solution 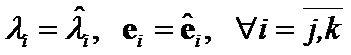 . According to the Hilbert theorem, for each
. According to the Hilbert theorem, for each ![]() and
and![]() exist unique
exist unique![]() and
and 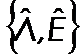 . If
. If 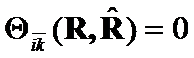 , then
, then ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Conclusion: The criteria 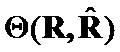 is a norm on
is a norm on ![]() .
.
Theorem 5. (symmetry)
If 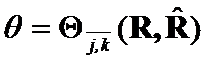 and
and 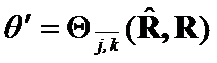 then
then![]() .
.
Proof: If ![]() and
and![]() switch places in
switch places in 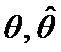 , then
, then ![]() .
.
Theorem 6.
If ![]() ,
, 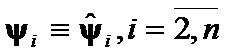 , then the
, then the 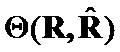 is the matrix norm difference
is the matrix norm difference
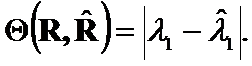
Proof:
Criteria 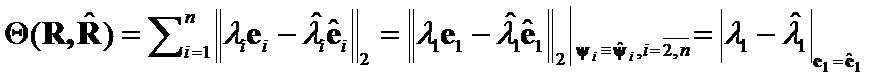 .
.
Theorem 7.
If  ,
, 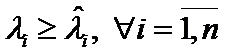 then
then 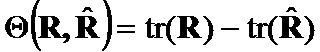 .
.
Proof:
From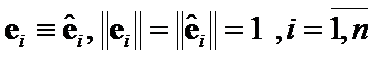 , and
, and 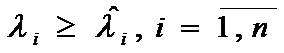 we received:
we received: